Hospice Care: How To Use The Karnofsky Performance Scale
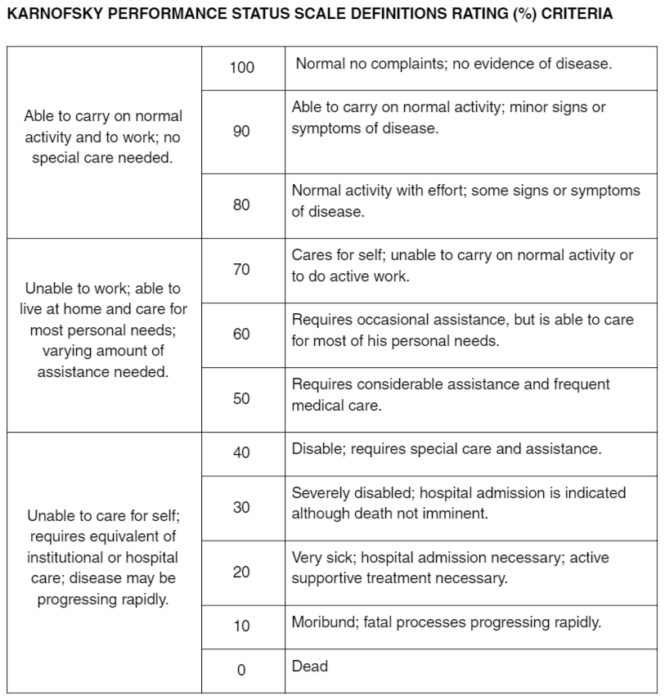
The Karnofsky Performance Scale, or KPS score, is an assessment tool for predicting of length of survival in terminally ill patients. The KPS scale is an 11 point rating system which ranges from normal functioning (100) to dead (0) in ten point increments. Use of these 11 points is necessary, meaning that estimates between points cannot be made.
Although no specific instructions were originally developed for administration of the KPS score, guidelines have recently been developed to assist in improving consistency and reliability of the scale. Research has suggested that seven variables account for a significant amount of variance in scoring of the KPS and represented all four categories of the KPS — evidence of disease, daily activity, self care and work.
Understanding the Karnofsky Scale: Scoring and Index Interpretation
The Karnofsky Scale, also known as the Karnofsky Performance Status or Karnofsky Index, is a numerical score that helps healthcare professionals assess a patient’s functional status. Each score on the Karnofsky Scale reflects a specific level of patient independence and physical ability.
The Karnofsky Scale is often utilized as a performance status score, offering a standardized way to evaluate a patient’s ability to perform daily tasks. KPS, the medical abbreviation for Karnofsky Performance Scale, is widely recognized among healthcare professionals. Here’s an over of the Karnofsky index:
- Origin and Development:
- The Karnofsky Index was developed by Dr. David A. Karnofsky as a way to quantify a cancer patient’s general well-being and functional status.
- It ranges from 0 to 100, with higher scores indicating better functional ability.
- Components of the Karnofsky Index:
- The index measures patient status across a spectrum, from normal functioning (100%) to severe disability or death (0%).
- Key points include the ability to carry out daily activities, requirement for medical care, and level of independence.
- Interpreting the Karnofsky Scores:
- Scores above 70% suggest a patient is able to care for themselves independently.
- Scores below 50% indicate significant disability, requiring considerable medical assistance.
- Applications in Hospice and Palliative Care:
- In hospice settings, the Karnofsky Index aids in determining the appropriate level of care and support needed for each patient.
- It is also instrumental in making informed decisions about treatment plans and gauging a patient’s response to therapy.
- Comparisons with Other Scales:
- While similar to the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status, the Karnofsky Index offers a more granular assessment of physical abilities.

Karnofsky Scale vs. Fast Score and PPS Scale in Hospice Care
In hospice care, the Karnofsky Scale is often compared with other tools like the FAST (Functional Assessment Staging Tool) Score and the PPS (Palliative Performance Scale) for comprehensive patient evaluation.
Karnofsky Performance Status (KPS):
- Scale Range: Ranges from 0 (death) to 100 (normal, no complaints, no signs of disease).
- Assessment Areas: Evaluate a patient’s physical ability, dependence on others, and daily activity levels.
- Usage in Care Planning: Helps determine the appropriate level of care and treatment options and estimate prognosis.
Palliative Performance Scale (PPS):
- Scale Design: A 10-point scale, each level representing a decreasing level of functional ability.
- Key Focus Areas: Assesses ambulation, activity, and evidence of disease, self-care, intake, and level of consciousness.
- Role in Palliative Care: Aids in assessing disease progression, planning care, and guiding discussions about end-of-life care.
Comparing KPS and PPS:
- Both scales measure a patient’s functional status but focus on slightly different aspects of care.
- KPS focuses more on general activities and independence, while PPS offers a more detailed look at specific physical abilities and care needs.
Using Performance Scales in Decision-Making:
- It helps healthcare professionals set realistic goals, manage expectations, and improve communication with patients and their families.
- It is crucial for tailoring treatment and care plans according to individual needs and abilities.
Calculators and Tools:
- Various online tools and calculators, such as the “palliative performance scale calculator” or “KPS score calculator,” are available to assist in accurately assessing these scales.
- This section highlights the utility of both KPS and PPS in providing comprehensive care to patients, especially those in hospice and palliative settings. Understanding these scales is fundamental for healthcare providers to deliver personalized and effective care.
CONTINUA LEARNING
Simplify Your Hospice Team’s Training and Skill Building
A complete solution for your agency: more than 125 hospice courses, caregiver in-services, training plans, and more.
When is the Karnofsky Performance Scale to be Completed?
- On admission to hospice, patients are to have a KPS completed if requested on the disease-specific Clinical Summary and when completing a General Summary. The KPS score is documented on the Clinical Summary as indicated.
- The KPS is to be completed for each recertification period if requested on the disease-specific Clinical Summary. The score is to documented where indicated on the clinical summary.
- The KPS is to be completed for a patient any time there are significant changes in status. The score should then be documented in the clinical note. Please be aware that the KPS has only been validated as a predictor of terminal decline in cancer and HIV patients. It can be completed for other patients if the score indicates a declining functional ability.
How to Complete the Karnofsky Performance Scale
- Review the scale: The Karnofsky Performance Scale ranges from 0-100 and is broken down into 10-point increments. The higher the score, the more independent the person is.
- Observe daily activities: Observe the patient’s ability to perform daily activities such as dressing, bathing, eating, and walking.
- Evaluate symptoms: Evaluate the patient’s symptoms, such as pain, shortness of breath, and nausea, and how they impact daily activities.
- Assign a score: Assign a score based on the patient’s ability to perform daily activities and their symptom severity. For example, a score of 100 indicates the person can perform all activities without assistance and has no symptoms. A score of 50 indicates the person is able to perform only half of their daily activities and has significant symptoms.
- Document the score: Document the score in the patient’s medical record and use it as a baseline for future assessments.
- Re-evaluate regularly: Re-evaluate the patient’s functional status and symptoms regularly, especially if there is a change in their condition.
- Use the scale in conjunction with other assessments: The Karnofsky Performance Scale should be used in conjunction with other assessments and clinical observations to provide a comprehensive evaluation of the patient’s functional status.
- Involve the patient and caregivers: Involve the patient and their caregivers in the assessment process to ensure accuracy and relevance.
- By following these steps, you can use the Karnofsky Performance Scale to assess a person’s independent functioning and track their progress over time.
The following questions can begin to serve as guidelines for determining the performance status of an individual patient.
Evidence of Disease:
- Has there been any weight loss or weight gain?
- Has there been any reduction in energy or increase in fatigue?
Self Care
- Has there been any difficulty grooming or bathing?
Daily Activities
- Has there been any difficulty in walking or moving around?
- Has there been any difficulty driving?
Work Difficulty
- Has there been any difficulty working full or part time?
The information obtained from these questions, the assessment and other medical data should then be used as specific criteria listed on the KPS Index. Once the criteria have been identified and the index which most closely corresponds to the criteria has been chosen, the KPS is documented. Following the admission assessment, when possible, the same health care provider should administer the scale on subsequent evaluations.
Comparative Analysis: Karnofsky Performance Status vs ECOG
Understanding the differences and similarities between the Karnofsky Performance Status (KPS) and the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) scale is crucial for healthcare professionals. This section delves into a comparative analysis of these two important scales:
Foundational Differences:
- KPS: Offers a detailed 11-point scale ranging from 0 (death) to 100 (normal, no complaints, no signs of disease).
- ECOG: Utilizes a simpler 5-point scale, from 0 (fully active) to 4 (completely disabled).
Scale Granularity and Usage:
- KPS: Provides a more nuanced assessment of a patient’s abilities and is often preferred in hospice and palliative care settings.
- ECOG: Due to its simplicity, it is widely used in oncology trials to assess a patient’s general well-being and ability to receive and respond to treatment.
Practical Application in Patient Assessment:
- Both scales are used to evaluate functional status, but the KPS offers a more detailed look at a patient’s ability to carry out daily life activities.
- ECOG is often preferred in clinical trials due to its straightforward approach.
Interpreting Scores for Patient Care:
- KPS: Scores below 50% often indicate a need for supportive care and possibly hospice consideration.
- ECOG: A score of 3 or 4 suggests severe disability, significantly impacting treatment decisions.
Clinical Implications in Decision-Making:
- Both scales are instrumental in guiding treatment plans, monitoring progression, and discussing prognosis with patients and families.
- Understanding how each scale measures patient performance status aids in providing tailored care and effective communication.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the KPS meaning?
The kps meaning is the ability of the Karnofsky Performance Scale to evaluate the functional status of terminally ill patients and estimate their expected survival length, as detailed in the guidelines provided on hospice care.
What is the Meaning and Definition of KPS in Medical Context?
KPS stands for Karnofsky Performance Scale, a system used to quantify a patient’s general well-being and ability to carry out daily activities, especially in the context of illness or medical treatment.
Is There a Calculator for the Palliative Performance Scale (PPS) Score?
While the Karnofsky Performance Scale doesn’t directly include a calculator, the Palliative Performance Scale (PPS), a related tool, often utilizes calculators to aid in patient assessment.
The Significance of a Negative KPS Meaning
A negative KPS meaning often indicates a severe deterioration in a patient’s health, where they cannot care for themselves. It’s crucial in hospice care to assess these scores accurately. This understanding assists healthcare providers in making informed decisions about patient care, particularly in advanced stages of illness.
How the FAST Score Relates to Hospice Care Alongside the KPS
The FAST score hospice system is another tool used alongside the Karnofsky score to evaluate patients in hospice care. It specifically assesses the functional decline in terminal illness. The FAST score complements the KPS by providing additional insights into the patient’s ability to perform daily activities, aiding in comprehensive patient assessment and care planning.
The Meaning of KPS Medical Abbreviation and Its Use in Hospice
KPS, or Karnofsky Performance Status, is a scale that helps assess a patient’s functional status and is widely used in hospice settings to determine the appropriate level of care. This scale is instrumental in evaluating how a patient’s illness impacts their daily life and independence, guiding healthcare professionals in tailoring care to each patient’s needs.


